Etiology
Susceptible Hosts
Cattle and Buffaloes are the most susceptible species. Young growing cattle and buffaloes within the age group of month to 2 years are most often affected. Sheep, goat, and pig may also suffer.
Mode of Transmission
Clinical Symptoms
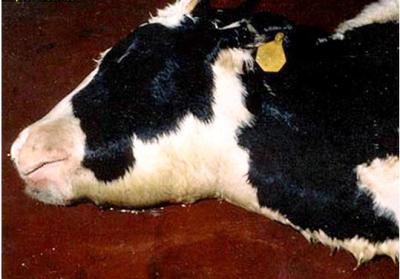
Septicaemic pasturellosis flares up as an outbreak during the environmental stress.The organism which remains in the tonsilles and nasopharyngeal mucosae assume the pathogenic role and there by set up clinical disease. The incubation period is 2 – 5 days. There is high rise in temperature 104 – 107 F with concurrent shivering followed by profuse salivation, lacrymation and nasal discharge. The affected animal exibit sign of abdominal pain,sever diarrhea. Rapid respiration. In less acute cases, there is rise in body temperature and localization of oedema in subcutaneous pockets of the head, neck, duwlop and brisket region. The oedema produce sever dyspnoea due to obstruction of respiratory passage. Death usually occur within 20-24 hours.
Control
The effective control lies with institution of adequate management, rational execution of vaccines and care in transportation of animal.
